通信系统建模与仿真——软件无线电基础、测量、案例及5G
软件无线电基础
软件无线电的核心理念
构造一个具有开放性、标准化、模块化的通用硬件平台,将各种功能,如工作频段、调制解调类型、数据格式、加密模式、通信协议等用软件来完成,并使A/D和D/A转换器尽可能靠近天线,以研制出具有高度灵活性、开放性的新一代无线通信系统。
软件无线电的核心技术
- 技术数字化 – ADC及DAC的广泛应用
- 平台通用化 – 高速ADC/DAC + DSP + FPGA
- 功能虚拟化 – 软件定义
- 结构总线化+模块化 – 定义标准化结构及接口
- 控制网络化
- 体系标准化
软件无线电的定义
软件定义无线电 (SDR) 的定义:其数字化是在天线端(或者非常接近)进行,无线电所需要的所有处理通过驻留在高速数字信号处理单元中的软件来实现--理想的软件无线电
软件无线电的特征
- 数字化是在天线端(或者非常接近)进行
- 大动态范围
- 多波段
- 多模式
- 软件不仅定义处理功能,也定义结构、模式和波段
软件无线电的系统描述
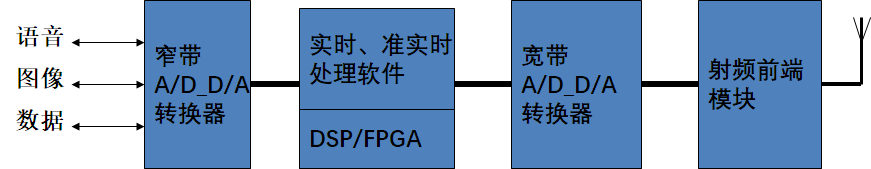
频谱测量及实际案例
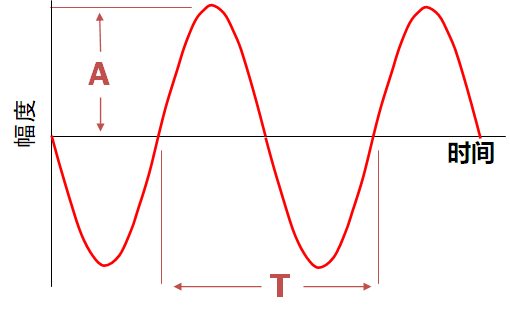
信号的时域观测:幅度 vs 时间
简单例子: 正弦波
- 纵轴为幅度
- 横轴为时间
- 频率为周期的倒数 (F = 1/T)
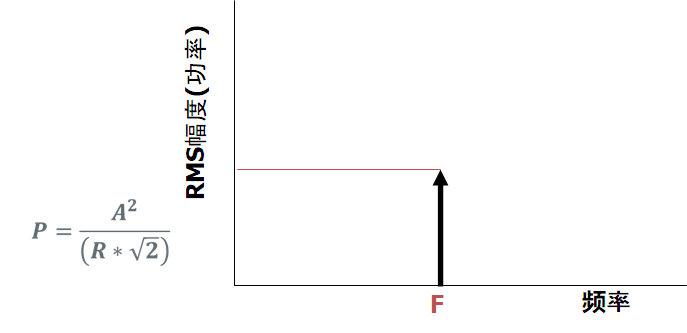
信号的频域观测:幅度 vs 频率
简单例子: 正弦波
- 纵轴为RMS幅度
- 横轴为频率
频谱分析仪实际上为指定频率的功率计
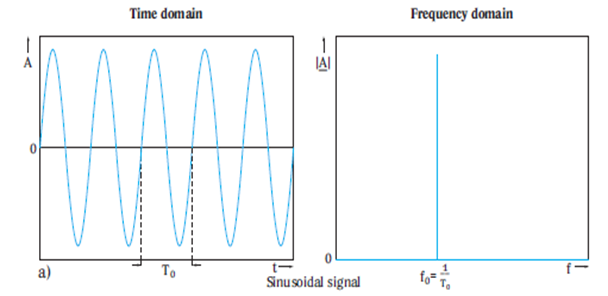
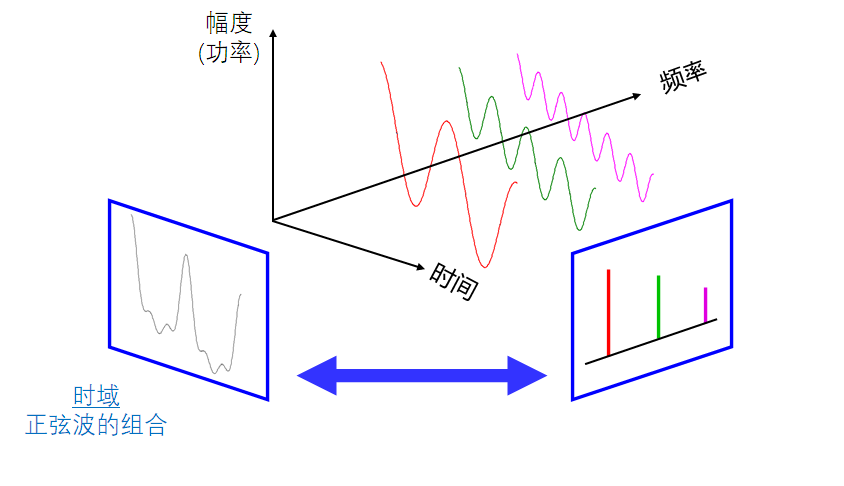
同一个信号不同观测维度
- 注意 – 电子不知道他们正在被什么设备进行观测
- 简单的正弦波例子
更多的例子 —— 方波
方波由许多正弦波构建而成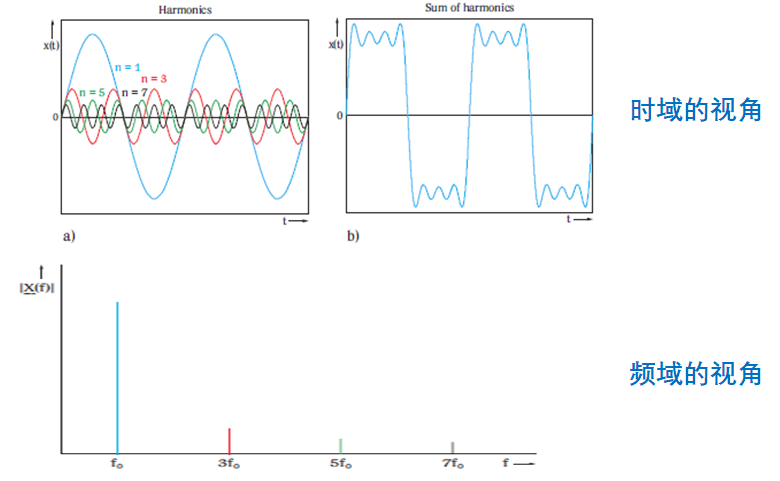
所有信号都可由一组正弦波构建而成
更多的例子
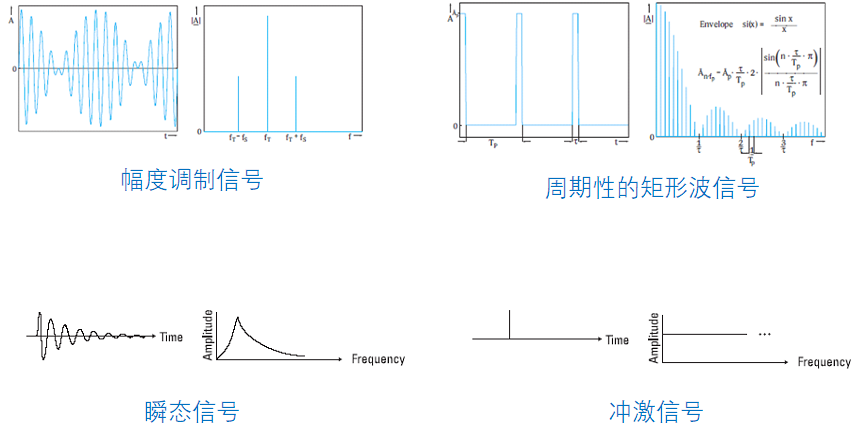
为什么要在频域观测信号?
噪声
- 任何东西都会产生噪声,它对整体设计的影响如何?
- 噪声的来源? (EMI)
- 信号对噪声的测量
失真
- 原则上在示波器上应该是纯净的正弦波可能包含谐波成分,但是在时域上可能并不明显,但是在频域上却能清晰的分辨
通信
- 现代无线通信技术自身源于频域
- 频段分配
- 定义通信信道
- 需要确认诸如占用带宽、调制质量等方面的性能
重要的频谱分析概念
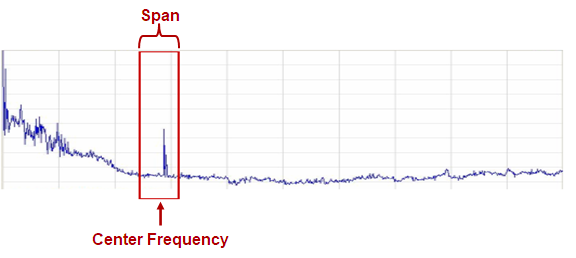
中心频率和分析范围 Center Frequency and Span
示波器FFT典型的分析方式是DC到to(采样率的一半)Hz
频谱分析仪的典型方法是设定一个中心频率CF(因为它在屏幕显示的中心)
- 典型的说法中心频率
在中心频率两侧可以观测的频率区域称作频率范围SPAN
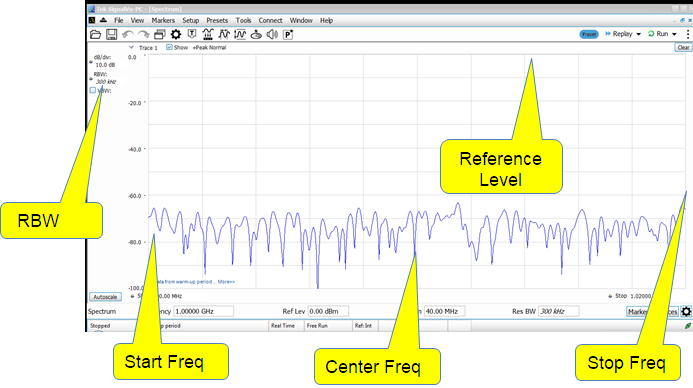
基本频谱分析仪界面
射频核心测量
| Measurements | Description |
|---|---|
| Channel Power | Is the device transmitting? On the correct channel? At the correct power? |
| Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio (ACLR) | Is the channel transmission spreading into an adjacent channels ? |
| Spectral Emissions Mask (SEM) | A broader check to ensure power stays within the intended channel |
| Spurious, Harmonics, Intermodulation | Is the device creating miscellaneous noise which may interfere with itself or others? |
| EMI Testing | What levels must the device fall within for radiated and conducted emissions so that it doesn’t interfere with others and can pass compliance? |
| Modulation Quality | Is the device talking clearly so that other receivers can hear it well? |
| Receiver Sensitivity & Blocking | Can the device receive its desired signals sufficiently and ignore others? |
| Impedance / Return Loss /VSWR | Are the modules impedance-matched so as to optimize operation ? |
Channel power, aclr
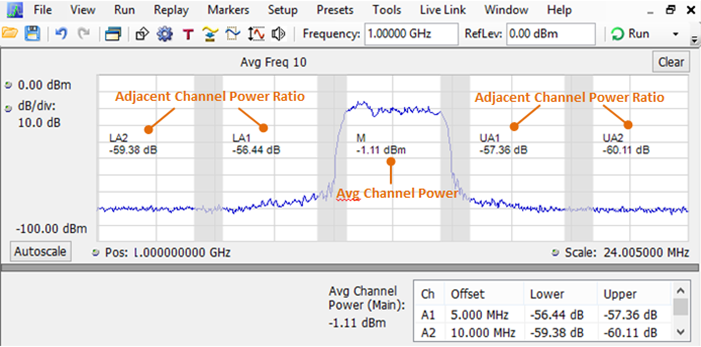
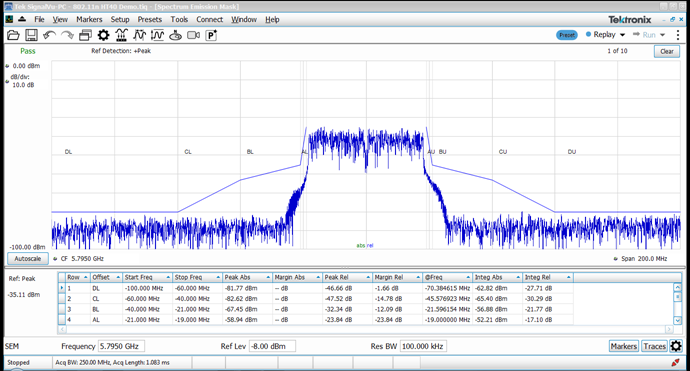
Spectral emissions mask
Spurious, harmonics, intermodulation
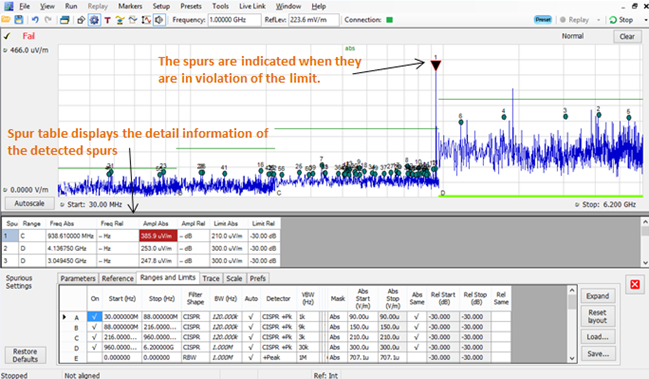
EMI Testing types and limits
EMI Pre-Compliance measurements are an approximation of the EMI signature of a product. Almost all products that use energy must pass some form of EMI testing. Products must be certified by an accredited test house before them may be sold in the market.
CISPR - an international body who specify EMI regulations. SVPC includes CISPR limit lines for many radiated and conducted specifications.
| Concern | Radiated | Wired (AC power) |
|---|---|---|
| Am I affecting others? | - Intentional radiated emissions - Unintentional radiated emissions |
Conducted emissions |
| Will I be affected by others? | electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS) |
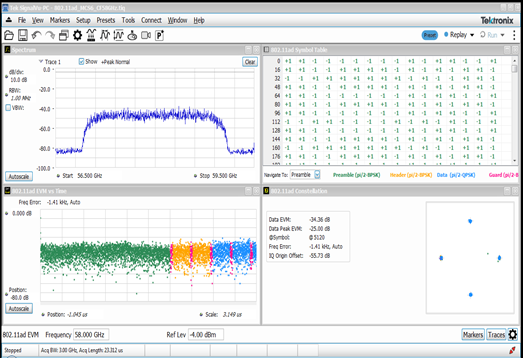
Modulation Quality – Tx Fidelity
Symbol Table - the data being transmitted, as determined by the demodulated signal.
Error Vector Magnitude (EVM) – a numerical calculation of modulation fidelity (how accurate the modulation is); zero is best.
Constellation Diagram – a visual representation of modulation fidelity (how accurate the modulation is); the clearer the diagriam the better.
Receiver Sensitivity and blocking test
Receiver sensitivity – how well your receiver can pick up small signals, which affects its range (distance) of operation. Usually measured as bit-error rate (BER) as a function of received power, or EVM as approximation.
Blocking - how well your receiver can receive the desired signal in the presence of unwanted signals.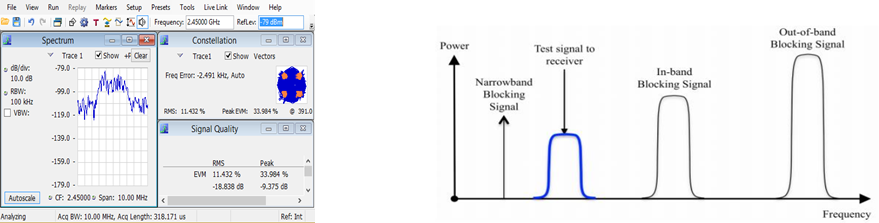
Impedance
- Impedance is a combination value which includes resistance and reactance
- Problem: Impedance is a dynamic value that can change based on frequency
- If there is a miss-match, some of the RF power that is being fed into a component (or cable, or antenna) will be reflected back to the source
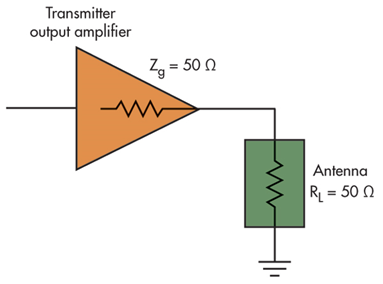
Voltage standing wave ratio (vswr)
- We want all the signal energy transferred from the transceiver to the antenna (or component) or vice versa (perfect impedance match at the antenna junction, i.e. a VSWR of 1:1)
- A short or open would reflect all energy back, creating standing waves in the signal
- Reality is somewhere in between, but hopefully closer to perfect energy transfer! VSWR tells us the amount of energy reflected

实时频谱发现1
提高发现偶发信号的概率 – POI
- Wi-Fi信号 + BLE信号
- 时间偶发
- 频率同频
实时频谱发现2
- 雷达信号 + 本振泄露
- 频率分布相同
- 能量高低不同
- 方向纵横交错 – 概率不同
实时频谱发现3
- 频率上拥挤重叠
- 阻断器
- 对抗环境
案例1:利用 DPX 发现 RFID 信号对 GSM 上行干扰
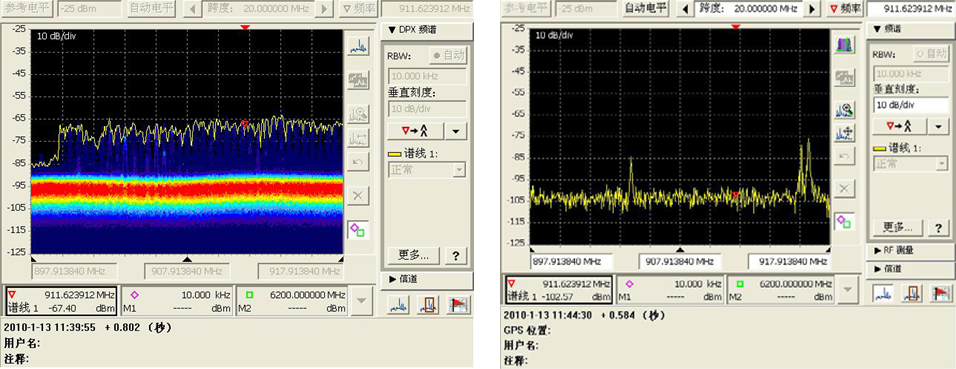
使用传统频谱仪无法对信号进行准确判断
RFID 门禁915MHz系统干扰GSM上行
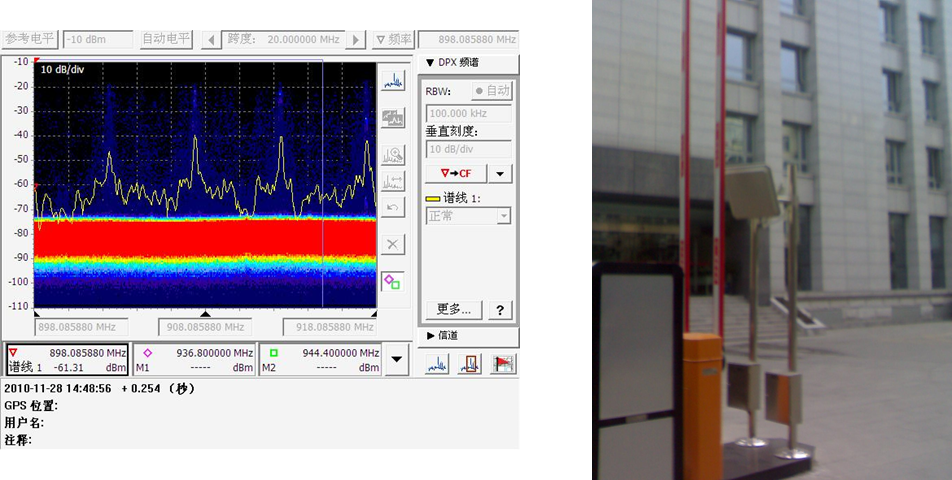
案例2:XX机场电磁环境测试
- 地空通信:AM调制 100MHz
- 底噪高:约-90dBm/Hz
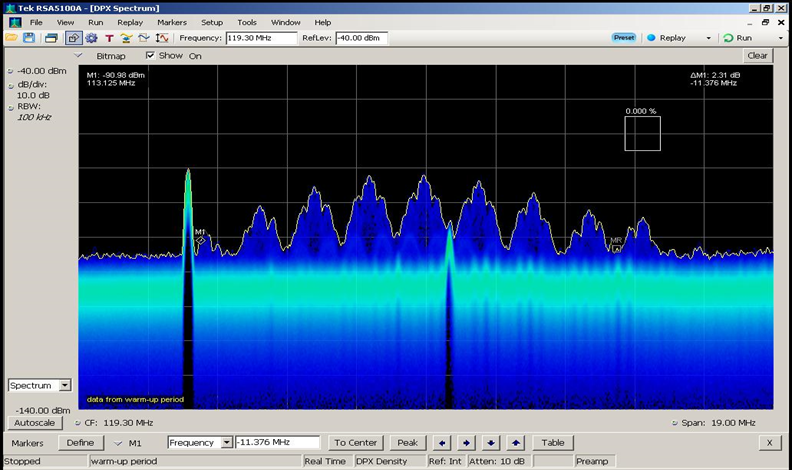
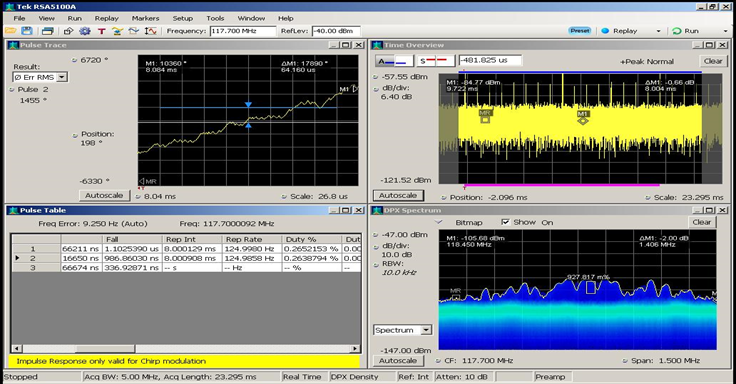
- 相位分析结果具有一定线性特征、时域波形规整
- “高脉冲”8ms重复一次、“矮脉冲”1ms重复一次
- 原因:米波雷达 – 远程预警
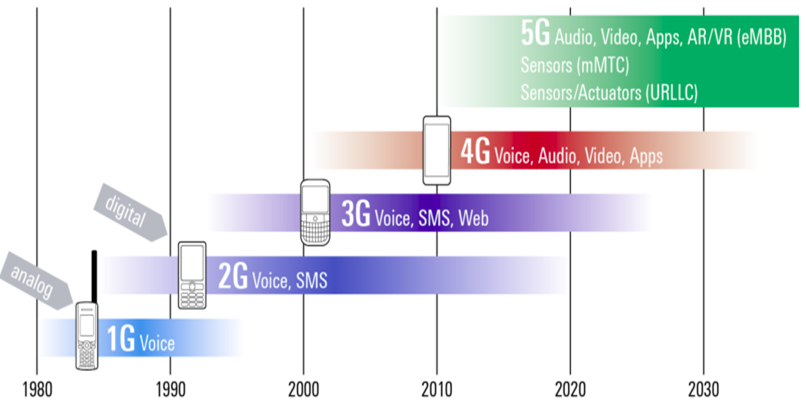
5G通信简介
5G技术介绍
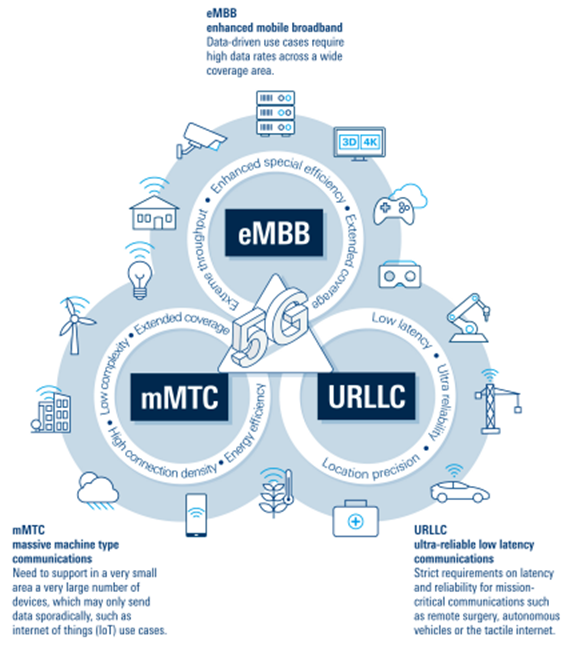
- eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband),增强移动宽带
- mMTC (massive Machine Type Communications),大规模物联网
- URLLC (Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications),低时延高可靠连接
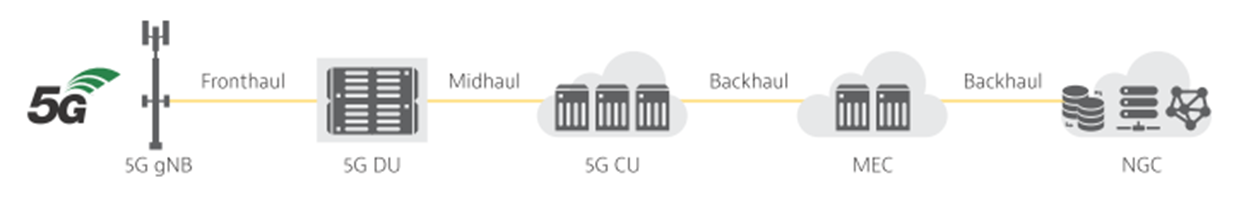
- DU (Distributed Unit),分布单元
- CU (Centralized Unit),集中单元
- MEC (Mobile Edge Computing),移动边缘计算
- NGC ( Next Generation Core),下一代核心网
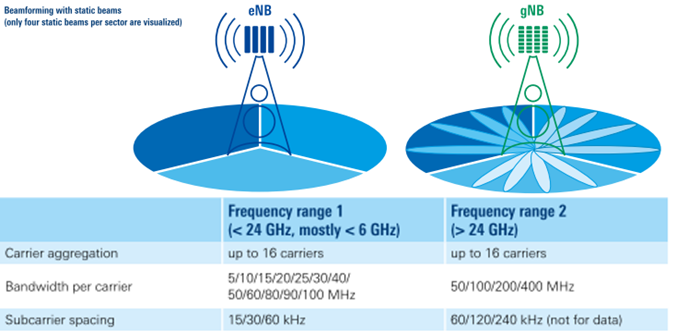
5G技术极大地提高了网络速度,缩短了连接时间。5G新无线电(NR)是3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) 标准,用于运行在低于7.125 GHz频段(FR1)和高于24.250 GHz毫米波频段(FR2)的无线网络。5G提供每秒千兆比特的数据速率。
5G网络使用更宽的带宽、更高的工作频率和有源天线系统,如相控阵天线。5G网络部署的关键挑战是描述空中接口路径损耗、优化波束覆盖和减少干扰问题。

我国5G技术频率划分
已商用网络频段
- 中国电信:3400MHz-3500MHz
- 中国联通:3500MHz-3600MHz
- 中国移动:2515MHz-2675MHz、4800MHz-4900MHz
已进行频率划分,正在部署的网络频段
- 700MHz频段:中国广电网络股份有限公司 (中国广电)
- 5.925GHz-7.125GHz/6.425GHz-7.125GHz频段:固定无线接入(FWA)



